In the field of healthcare, hospital beds and home nursing beds are two of the most common types of beds. They differ significantly in structural design, functional configuration, usage environment, and operation.
For many patients' families, healthcare procurement personnel, and even elderly care service providers, understanding the differences between these two types of beds is crucial for selecting appropriate equipment and improving care efficiency.
This article will analyze the differences between hospital beds and home nursing beds from multiple perspectives, including structure, function, safety, ease of operation, usage location, material design, and cost and maintenance, to help readers make a scientific and rational choice.
Why differentiate between hospital beds and home nursing beds?
Many people believe that hospital beds and home nursing beds are simply "different in their usage location," but this view is overly simplistic. In fact, the design philosophies of these two types of beds are completely different.
• The core objective of a hospital bed is to meet the high-intensity clinical care needs within a hospital. It must possess high stability, sterilizability, and functional integration to adapt to use by doctors and nurses in different environments such as emergency rooms, intensive care units, and rehabilitation centers.
• The core objective of a home nursing bed is to provide patients with a comfortable, safe, and convenient long-term care experience in a home environment. It emphasizes user comfort, ease of operation for caregivers, and adaptability to home spaces.
Therefore, distinguishing between the two not only helps in scientific selection but also effectively avoids resource waste and care risks.
Hospital Beds and Home Nursing Beds: What are the differences in structural design?
1. Bed Structure Stability and Load-Bearing Capacity
Hospital beds typically use thickened carbon steel, medical-grade stainless steel, or high-strength aluminum alloy to withstand frequent lifting, turning, and equipment suspension. Their load-bearing capacity generally reaches 250–350 kg, with some ICU beds even exceeding 400 kg.
Home care beds prioritize lightweight design and portability. Most utilize a combination of spray-painted steel tubing and ABS plastic headboard and footboard, with a weight capacity typically between 150-250 kg, sufficient for general home care but unsuitable for long-term use by critically ill or overweight patients.
2. Number of Adjustable Functions
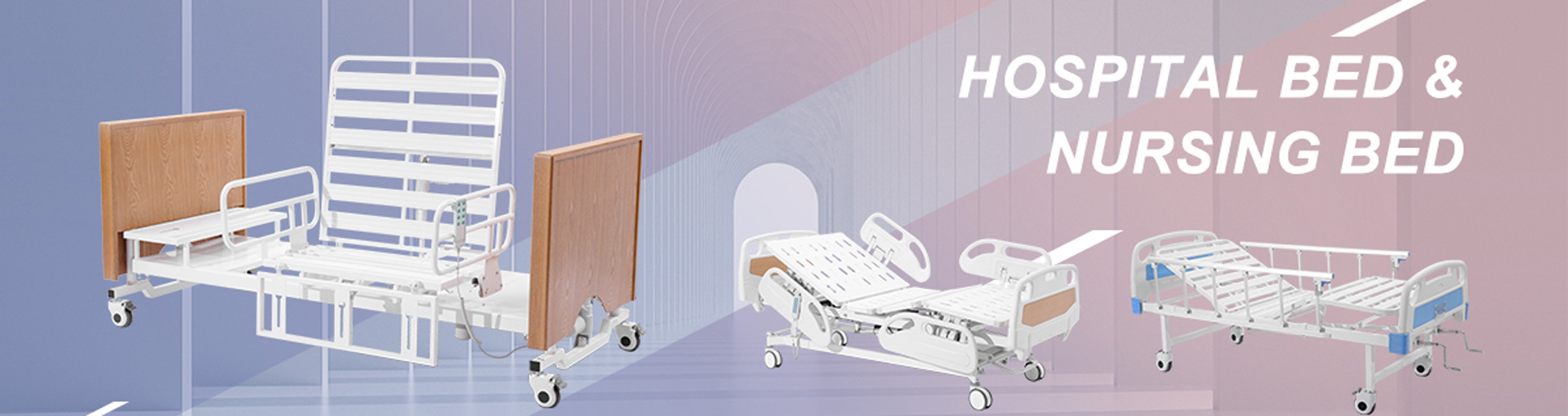
Hospital beds usually feature multi-stage electric adjustment systems, including backrest height adjustment, legrest height adjustment, overall height adjustment, tilting, and repositioning functions. Higher-end models may also include CPR functionality, a one-button zeroing system, and an electronic weighing system.
Home care beds have relatively simpler functions, commonly featuring backrest height adjustment, legrest height adjustment, and overall height adjustment. Some models may include side-turning or bedpan drawer functions, but overall, they primarily cater to basic nursing needs.

Hospital Beds vs. Home Care Beds: What are the differences in control methods?
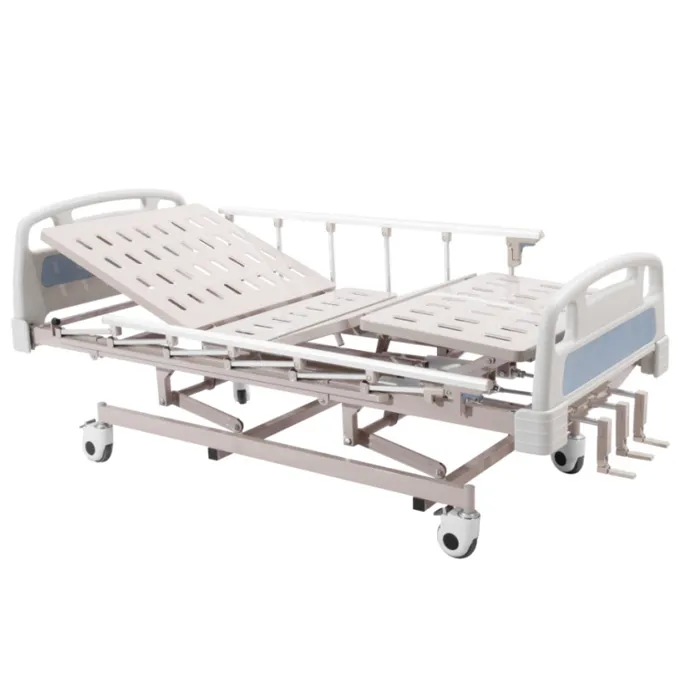
Hospital beds generally use a centralized electric control system, equipped with a wired handheld controller or nurse control panel, and can even be remotely adjusted via a central control console or wireless network connection. This system ensures that medical staff can quickly adjust the bed's position to meet emergency care needs.
Home care beds, on the other hand, prioritize ease of operation and user experience. Most home care beds are equipped with wireless remote controls or handheld wired controllers, with clear buttons and intuitive operation logic, making them convenient for family members or patients to use directly. Some products also feature voice prompts or app control functions, adapting to smart home usage habits.
In short, hospital beds prioritize "multifunctionality and high efficiency," while home care beds prioritize "humanization and convenience."
What are the differences in safety performance between hospital beds and home care beds?
1. Protection and Safety Standards
Hospital beds must meet strict medical device safety standards (such as IEC 60601-2-52), requiring emergency power-off protection, anti-pinch design, electrostatic protection, and mechanical safety locking mechanisms. Their bed rail design meets clinical fall prevention standards and is equipped with an electrical safety isolation system.
Home care beds have relatively more lenient safety standards, but still prioritize human safety and ease of care. It typically features bed rails, braked casters, and non-slip mattresses, but has lower requirements for electrical protection and clinical-grade safety isolation.
2. Electric System Stability
Hospital beds mostly use medical-grade motors (such as LINAK and Dewert brands), which are highly durable and low-noise, capable of continuous operation for thousands of hours.
Home care beds may use mid-range motor systems, requiring only adjustments for daily care, with noise levels controlled below 50dB, emphasizing comfort.
Hospital Beds and Home Care Beds: What are the differences in usage scenarios?
1. Application Locations of Hospital Beds
Hospital beds are mainly used in hospital wards, ICUs, post-operative rehabilitation wards, and hospice wards. They must support the connection of various medical instruments (such as IV stands, monitors, oxygen interfaces, traction frames, etc.) and withstand high-intensity disinfection and frequent movement.
2. Usage Scenarios of Home Care Beds
Home care beds are widely used in family bedrooms, nursing homes, and community rehabilitation centers. Due to limited installation space, hospital beds are designed to be more compact, and some models also feature folding mechanisms, wheeled movement systems, or silent operation to suit the quiet environment and space constraints of a home.
In summary, hospital beds are professional medical equipment, while home care beds are assistive living devices; this is the fundamental difference in their usage environments.
Is there a significant price difference between hospital beds and home care beds?
Price is one of the most important concerns for many buyers.
• Hospital bed price range: Basic manual hospital beds cost approximately $1,000–$2,000, while electric multi-functional beds generally range from $3,000 to $5,000, with high-end ICU beds exceeding $10,000.
• Home care bed price range: Manual beds typically cost $500–$1,500, electric multi-functional beds cost approximately $2,000–$3,000, and feature-rich models (with turning or commode functions) can be purchased for under $5,000.
The main reason for this difference is that hospital beds have significantly higher costs for their medical-grade electrical systems, protective designs, material grades, and certifications compared to home care beds.
Which is more suitable for long-term use: a hospital bed or a home care bed?
For critically ill patients, post-operative recovery, or those requiring frequent medical procedures, hospital beds are undoubtedly more suitable. They offer greater stability and operational precision, supporting medical staff in performing various treatments.
However, for elderly people who are bedridden for extended periods, patients with chronic diseases, or those requiring home care, home care beds are more suitable. They are not only more comfortable and easier to operate, but also reduce the physical burden on home caregivers.
The key to choosing a home care bed lies in the intensity of care needs and environmental conditions—hospital beds are preferred for high medical needs, while home care beds are preferred for primary daily care.

Are there differences in the mobility of hospital beds and home care beds?
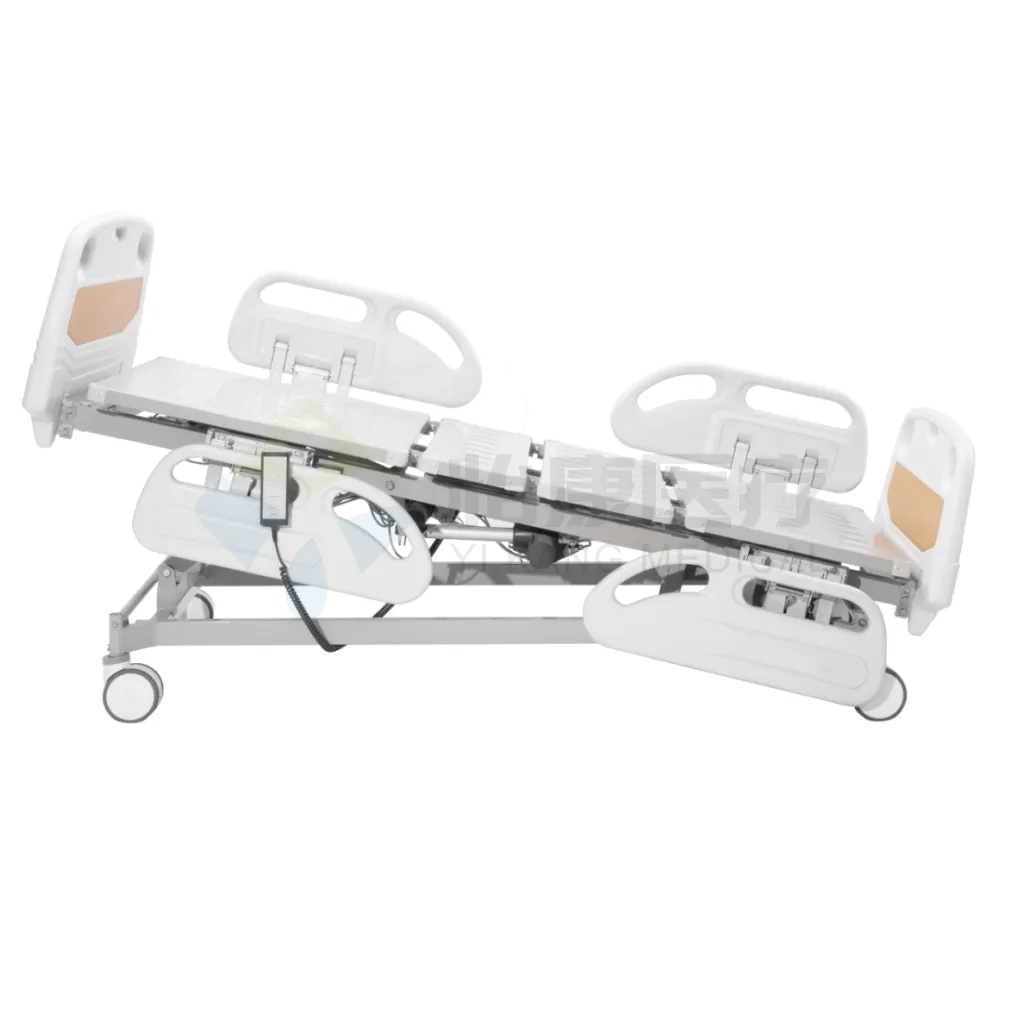
Hospital beds are generally equipped with medical-grade silent casters with a central braking system, allowing for easy movement within the ward and quick locking into position. Movement should be smooth, noiseless, and easy to push.
Home care beds typically use lightweight casters or detachable wheels, primarily for short-distance movement or easy cleaning. They are lighter in weight but not suitable for frequent relocation.
How to choose between hospital beds and home care beds?
When choosing, consider the following factors:
• User's condition: Does the patient require frequent care, monitoring, or treatment?
• Usage environment: Space size, floor levelness, power supply location, etc.
• Operators: Will the bed be operated by medical staff or cared for by family members?
• Budget range: Plan reasonably based on the usage period and financial capacity.
General recommendations:
• Hospital beds are recommended for medical institutions and rehabilitation centers;
• Home care beds are recommended for home care and elderly care;
• If the patient needs long-term bed rest but does not require frequent medical procedures, a medical-grade home care bed can be considered, balancing functionality and comfort.

A Summary of the Key Differences Between Hospital Beds and Home Care Beds
Comparison Items | Hospital Bed | Home Nursing Bed |
| Application Location | Hospital, Rehabilitation Center, ICU | For homes, nursing homes, and community care centers |
| Load Capacity | High (250–400kg) | Medium (150–250kg) |
| Adjustment Method | Multi-functional Electric/Centralized Control | Manual or simple electric |
| Number of Functions | Multiple Treatment Supports | Primarily for basic care |
| Safety Standards | Medical Device Standards | Home safety standards |
| Design Style | Industrialized, Standardized | Home-like and comfortable |
Price Range | Mid-to-High-End | Economy to mid-range |
| Maintenance and Cleaning | High-Frequency Professional Sterilization | Easy to clean for home use |
In summary, hospital beds are geared towards professional medical use, while home care beds aim to provide comfortable and safe long-term care in a home setting. Neither is inherently superior; the key is whether it matches the actual needs of the user.
What Types of Hospital Furniture Does Yikang Supply?
We provide a wide range of hospital furniture, including electric hospital beds, manual nursing beds, adjustable commode chairs, overbed tables, IV poles, and patient transfer aids. Our products are suitable for hospitals, rehabilitation centers, nursing homes, and home care use. All furniture is built using high-quality materials and ergonomic design principles to support patient safety and caregiver convenience.

